EvalVid NS2 Wireless
Best Project topics on EvalVid NS2 WirelessEvalVid NS2 Wireless:
Wireless is a more modern alternative to traditional wired networking that relies on cables to connect network able devices.In wireless network domain, video transmission is a current research topic which is widely chosen by academic students.
Features of wireless network:
- Provide multicast services.
- Network management services.
- Accommodation of transmission rates of 1 and 2 Mbps.
- Registration and authentication services.
- Support of asynchronous and time-bounded delivery service.
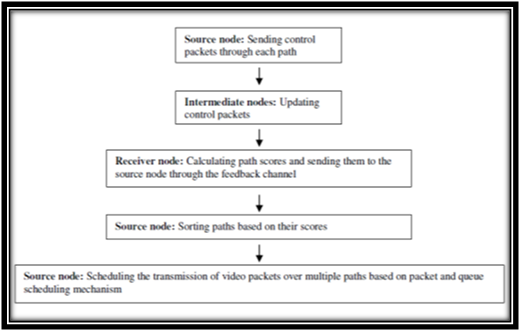
Challenges on wireless network:
- Improve quality of service in wireless network.
- Introduce Adaptive Feedback Algorithm for Internet Video Streaming based on Fuzzy Control.
- Effective EMPEG video transmission over wireless network.
- Transmission of video streams.
- Define congestion control schemes.
NS2 Projects Video Output
See our Latest Video Output of Ns2 Projects on Various Domain.
Ns2 Projects
Customized NS2 Projects for B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech/Ms/PhD Scholars.
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots.Regular Update of NS2 Projects Screenshots here!
Sample code for Evalvid ns2 wireless
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#ifdef _WIN32
#include "stdint_w32.h"
#define alloca _alloca
#else
#include <stdint.h>
#endif
#define x264_alloca(x) (void*)(((intptr_t)alloca((x)+15)+15)&~15)
#define XCHG(type,a,b) { type t = a; a = b; b = t; }
#define X264_MIN(a,b) ( (a)<(b) ? (a) : (b) )
static void ssim_4x4x2_core( const uint8_t *pix1, int stride1,
const uint8_t *pix2, int stride2,
int sums[2][4])
{
int x, y, z;
for(z=0; z<2; z++)
{
uint32_t s1=0, s2=0, ss=0, s12=0;
for(y=0; y<4; y++)
for(x=0; x<4; x++)
{
int a = pix1[x+y*stride1];
int b = pix2[x+y*stride2];
s1 += a;
s2 += b;
ss += a*a;
ss += b*b;
s12 += a*b;
}
sums[z][0] = s1;
sums[z][1] = s2;
sums[z][2] = ss;
sums[z][3] = s12;
pix1 += 4;
pix2 += 4;
}
}
static float ssim_end1( int s1, int s2, int ss, int s12 )
{
static const int ssim_c1 = (int)(.01*.01*255*255*64 + .5);
static const int ssim_c2 = (int)(.03*.03*255*255*64*63 + .5);
int vars = ss*64 - s1*s1 - s2*s2;
int covar = s12*64 - s1*s2;
return (float)(2*s1*s2 + ssim_c1) * (float)(2*covar + ssim_c2)\
/ ((float)(s1*s1 + s2*s2 + ssim_c1) * (float)(vars + ssim_c2));
}
static float ssim_end4( int sum0[5][4], int sum1[5][4], int width )
{
int i;
float ssim = 0.0;
for( i = 0; i < width; i++ )
ssim += ssim_end1( sum0[i][0] + sum0[i+1][0] + sum1[i][0] + sum1[i+1][0],
sum0[i][1] + sum0[i+1][1] + sum1[i][1] + sum1[i+1][1],
sum0[i][2] + sum0[i+1][2] + sum1[i][2] + sum1[i+1][2],
sum0[i][3] + sum0[i+1][3] + sum1[i][3] + sum1[i+1][3] );
return ssim;
}
float x264_pixel_ssim_wxh(
uint8_t *pix1, int stride1,
uint8_t *pix2, int stride2,
int width, int height )
{
int x, y, z;
float ssim = 0.0;
int (*sum0)[4] = x264_alloca(4 * (width/4+3) * sizeof(int));
int (*sum1)[4] = x264_alloca(4 * (width/4+3) * sizeof(int));
width >>= 2;
height >>= 2;
z = 0;
for( y = 1; y < height; y++ )
{
for( ; z <= y; z++ )
{
XCHG( void*, sum0, sum1 );
for( x = 0; x < width; x+=2 )
ssim_4x4x2_core( &pix1[4*(x+z*stride1)], stride1, &pix2[4*(x+z*stride2)], stride2, &sum0[x] );
}
for( x = 0; x < width-1; x += 4 )
ssim += ssim_end4( sum0+x, sum1+x, X264_MIN(4,width-x-1) );
}
return ssim / ((width-1) * (height-1));
}
int main(int n, char *cl[])
{
FILE *f1, *f2;
int ssim = 0, i, x, y, yuv, inc = 1, size = 0, N = 0, Y, F;
double yrmse, diff, mean = 0, stdv = 0, *ypsnr = 0;
unsigned char *b1, *b2;
clock_t t = clock();
if (n != 6 && n != 7) {
puts("psnr x y <YUV format> <src.yuv> <dst.yuv> [multiplex] [ssim]");
puts(" x\t\tframe width");
puts(" y\t\tframe height");
puts(" YUV format\t420, 422, etc.");
puts(" src.yuv\tsource video");
puts(" dst.yuv\tdistorted video");
puts(" [multiplex]\toptional");
puts(" [ssim]\toptional: calculate structural similarity instead of PSNR");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if ((f1 = fopen(cl[4], "rb")) == 0) goto A;
if ((f2 = fopen(cl[5], "rb")) == 0) goto B;
if (!(x = strtoul(cl[1], 0, 10)) ||
!(y = strtoul(cl[2], 0, 10))) goto C;
if ((yuv = strtoul(cl[3], 0, 10)) > 444) goto D;
if (cl[6] && !strcmp(cl[6], "multiplex")) inc = 2;
if (cl[6] && !strcmp(cl[6], "ssim")) ssim = 1;
Y = x * y;
switch (yuv) {
case 400: F = Y; break;
case 422: F = Y * 2; break;
case 444: F = Y * 3; break;
default :
case 420: F = Y * 3 / 2; break;
}
if (!(b1 = malloc(F))) goto E;
if (!(b2 = malloc(F))) goto E;
for (;;) {
if (1 != fread(b1, F, 1, f1) || 1 != fread(b2, F, 1, f2)) break;
if (++N > size) {
size += 0xffff;
if (!(ypsnr = realloc(ypsnr, size * sizeof *ypsnr))) goto E;
}
if (ssim) {
mean += ypsnr[N - 1] = x264_pixel_ssim_wxh(b1, x, b2, x, x, y);
} else {
for (yrmse = 0, i = inc - 1; i < (inc == 1 ? Y : F); i += inc) {
diff = b1[i] - b2[i];
yrmse += diff * diff;
}
mean += ypsnr[N - 1] = yrmse ? 20 * (log10(255 / sqrt(yrmse / Y))) : 0;
}
printf("%.3f\n", ypsnr[N - 1]);
}
if (N) {
mean /= N;
for (stdv = 0, i = 0; i < N; i++) {
diff = ypsnr[i] - mean;
stdv += diff * diff;
}
stdv = sqrt(stdv / (N - 1));
free(ypsnr);
}
fclose(f1);
fclose(f2);
fprintf(stderr, "%s:\t%d frames (CPU: %lu s) mean: %.2f stdv: %.2f\n",
ssim ? "ssim" : "psnr", N, (unsigned long) ((clock() - t) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC), mean, stdv);
return 0;
fprintf(stderr, " Error opening source video file.\n"); goto X;
fprintf(stderr, " Error opening decoded video file.\n"); goto X;
fprintf(stderr, " Invalid width or height.\n"); goto X;
fprintf(stderr, " Invalid YUV format.\n"); goto X;
fprintf(stderr, " Not enough memory.\n");
X: return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
Journal Support for Research Scholars

Ns2 Projects Work Progress
- MANET – Mobile Ad Hoc Network 95%
- VANET – Vechicle Ad Hoc Netwok 97%
- LTE – Long Term Evolution 78%
- IoT – Internet of Things 90%
- Wireless Sensor Network 89%
- Network Security 89%
- Ns2 Attacks 96%
- Cognitive Radio Network 85%
- Parallel and Distributed Computing 73%
- SDN – Software Defined Networking 95%
- P2P , Video Streaming , Peersim 96%
- IPV4 , IPV6 88%
- 4G Network , 5G Network 80%
- Visual , Underwater Sensor Network 79%
- Multicasting Communication 84%
- Wimax, WiFi 90%
- OFDMA 94%
Our Achievements – Ns2 Projects

