NS2 TCP Congestion Control
How to simulate TCP Congestion Control using NS2 simulator?What is TCP Congestion Control?
Congestion control is a state in which a part of a network message traffic is so heavy that it slows down network response time.When one part of the subnet (e.g. one or more routers in an area) becomes overloaded, congestion results.Congestion control is a global issue which involves every host and router within the subnet becomes overloaded.
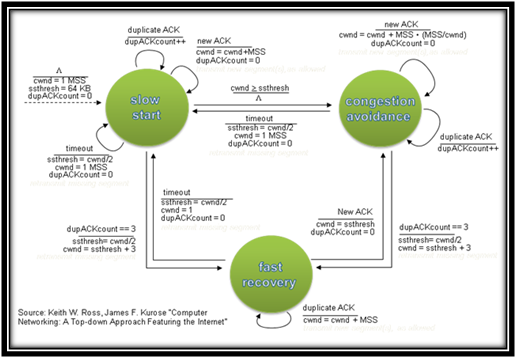
TCP congestion control algorithms:
- Slow start.
- Fast recovery.
- Network pricing.
- Congestion avoidance.
- Fast retransmit.
- TCP paging.
- Selective acknowledgment.
- Random early detection.
Goals of tcp congestion control:
- To increase the source send rate when the network is not congested.
- To share the network resources with other TCP flows in a “fair” way.
- To reduce the source send rate when the network is congested.
Types of message level description available in TCP congestion control:
- TCP Reno source.
- TCP Sink.
- TCP Tahoe source.
NS2 Projects Video Output
See our Latest Video Output of Ns2 Projects on Various Domain.
Ns2 Projects
Customized NS2 Projects for B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech/Ms/PhD Scholars.
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots.Regular Update of NS2 Projects Screenshots here!
Sample code for TCP congestion control:
This is the code for packets handled in tcp congestion control
class PacketData : public AppData {
public:
PacketData(int sz) : AppData(PACKET_DATA) {
datalen_ = sz;
if (datalen_ > 0)
data_ = new unsigned char[datalen_];
else
data_ = NULL;
}
PacketData(PacketData& d) : AppData(d) {
datalen_ = d.datalen_;
if (datalen_ > 0) {
data_ = new unsigned char[datalen_];
memcpy(data_, d.data_, datalen_);
} else
data_ = NULL;
}
virtual ~PacketData() {
if (data_ != NULL)
delete []data_;
}
unsigned char* data() { return data_; }
virtual int size() const { return datalen_; }
virtual AppData* copy() { return new PacketData(*this); }
private:
unsigned char* data_;
int datalen_;
};
Journal Support for Research Scholars

Ns2 Projects Work Progress
- MANET – Mobile Ad Hoc Network 95%
- VANET – Vechicle Ad Hoc Netwok 97%
- LTE – Long Term Evolution 78%
- IoT – Internet of Things 90%
- Wireless Sensor Network 89%
- Network Security 89%
- Ns2 Attacks 96%
- Cognitive Radio Network 85%
- Parallel and Distributed Computing 73%
- SDN – Software Defined Networking 95%
- P2P , Video Streaming , Peersim 96%
- IPV4 , IPV6 88%
- 4G Network , 5G Network 80%
- Visual , Underwater Sensor Network 79%
- Multicasting Communication 84%
- Wimax, WiFi 90%
- OFDMA 94%
Our Achievements – Ns2 Projects

