Research Topics on NS2
Current Research Topics On NS2 ? Implementing NS2 Code ?
Ns2 is a network simulation tool. By using this tool the researchers simulates their research in network. The following network research area are discussed as follows,
- Cognitive radio network (Research Topics on NS2).
- Robotic sensor network(Research Topics on NS2).
- Optical network(Research Topics on NS2).
- WSAN(Research Topics on NS2).
- 5G Network(Research Topics on NS2).
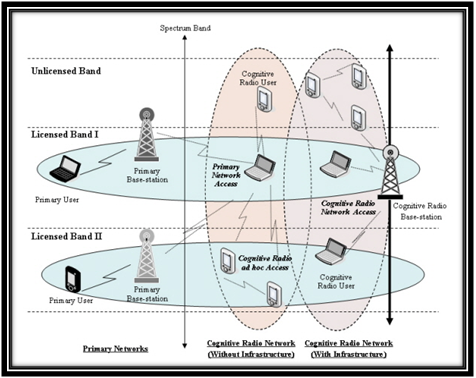
Cognitive radio network:
- Cognitive Radio (CR) is an adaptive, intelligent radio and network technology that can automatically detect available channels in a wireless spectrum and change transmission parameters.
- Cognitive radio technology enables radio devices to use spectrum in entirely new and sophisticated ways
Types of cognitive radio:
- Spectrum sharing type cognitive radio
- Heterogeneous-type cognitive radio
Fundamentals of cognitive radio:
- Ability to sense environment
- Evaluate options
- implement chosen waveform
Advantages of CRN:
- improve QoS
- improved spectrum utilization etc
Research issues on CRN:
- spectrum sensing
- signal processing
- packet routing
- predictive modeling
- security
- Transmit-power control system etc.
NS2 Projects Video Output
See our Latest Video Output of Ns2 Projects on Various Domain.
Ns2 Projects
Customized NS2 Projects for B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech/Ms/PhD Scholars.
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots.Regular Update of NS2 Projects Screenshots here!
Sample code for CRN:
This is the sample code for path selection procedure in the cognitive radio network.
Path::Path(int route_len, const ID *route)
{
path = new ID[MAX_SR_LEN];
assert(route_len <= MAX_SR_LEN);
// route_len = (route == NULL : 0 ? route_len);
// a more cute solution, follow the above with the then clause
if (route != NULL)
{
for (int c = 0; c < route_len; c++)
{
path[c] = route[c];
}
len = route_len;
}
else
{
len = 0;
}
cur_index = 0;
max_ps_level_ = 0;
max_ps_level_valid_ = false;
}
Path::Path()
{
path = new ID[MAX_SR_LEN];
len = 0;
cur_index = 0;
max_ps_level_ = 0;
max_ps_level_valid_ = false;
}
Path::Path(const struct sr_addr *addrs, int len)
{
/* make a path from the bits of an NS source route header */
assert(len <= MAX_SR_LEN);
path = new ID[MAX_SR_LEN];
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) path[i] = ID(addrs[i]); this->len = len;
cur_index = 0;
max_ps_level_ = 0;
max_ps_level_valid_ = false;
}

Optical network:
Optical networks are high-capacity telecommunications networks based on optical technologies and components that provide routing, grooming and restoration at the wavelength level as well as wavelength-based services.
Types of optical networking:
- Synchronous optical networking.
- Star networking.
- Passive optical network.
Research issues of optical networks:
- Fault localization.
- Define efficient centralized or distributed scheduling.
- MONET (Multi wavelength Optical Networking).
- To provide high bandwidth services.
- Multi-wavelength transport network.
Benefits of optical network:
- Connectivity of the optical networking is more efficient as compared to other connections between the networks
- Optical networks are faster as compared to other mode of transmission of data between distances.
- Co axial cables are also used for the data transmission purposes but they are quite slow
- It’s more reliable and convenient fro the users to enjoy the facility of the transmission from different places at large distances because all the data is wrapped in the core of fiber optics.

WSAN:
- Wireless sensor and actor networks (WSANs) refer to a group of sensors and actors linked by wireless medium to perform distributed sensing and actuation tasks.
- In such a network, sensors gather information about the physical world, while actors take decisions and then perform appropriate actions upon the environment, which allows remote, automated interaction with the environment.
Applications of WSAN:
- Precision agriculture
- Home and assisted living medical care
- Industrial automation
- Global scale environmental monitoring
- Numerous military applications
- Smart building and cities etc.
Research areas of WSAN:
- Designing cross layering approach
- Define efficient task allocation mechanism
- To decrease communication delay between sensing and acting
- Design energy efficiency in WSAN
- Real time applications etc.
Features of wireless sensor and actor network:
- A distributed local coordination mechanism is necessary among the WSAN for providing effective sensing and acting
- WSAN are usually resource-rich devices equipped with better processing capabilities, stronger transmission powers and longer battery life.
- Depending upon the application there may be a need to rapidly respond to sensor input
- It does not require dense deployment area due to the different coverage requirements and physical interaction methods of acting task.
- In WSAN the number of actors is much lower than the sensors.
Sample code for WSAN:
This is the code for calling mac layer in cross layer approach. In WSAN designing cross layer is one of the research area.
nt id = (u_int32_t)addr();
Tcl&tcl = Tcl::instance();
tcl.evalf("$sensoragent_(%d) access-sinkTable",id);
const char* sp = tcl.result();
char a[7][30];
int k = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
k++;
int j = 0;
while(sp[k] != ',') {
a[i][j] = sp[k];
j++;
k++;
}
a[i][j] = '\n';
}
(Or)
const char* sp = tcl.result();
int i=0;
char *tokenPtr, *a[7];
char stl_current[strlen(sp)+1];
strcpy(stl_current, sp);
tokenPtr = strtok(stl_current, ",");
while(tokenPtr != NULL) {
a[i++] = tokenPtr;
tokenPtr = strtok(NULL, ",");
}
Journal Support for Research Scholars

Ns2 Projects Work Progress
- MANET – Mobile Ad Hoc Network 95%
- VANET – Vechicle Ad Hoc Netwok 97%
- LTE – Long Term Evolution 78%
- IoT – Internet of Things 90%
- Wireless Sensor Network 89%
- Network Security 89%
- Ns2 Attacks 96%
- Cognitive Radio Network 85%
- Parallel and Distributed Computing 73%
- SDN – Software Defined Networking 95%
- P2P , Video Streaming , Peersim 96%
- IPV4 , IPV6 88%
- 4G Network , 5G Network 80%
- Visual , Underwater Sensor Network 79%
- Multicasting Communication 84%
- Wimax, WiFi 90%
- OFDMA 94%
Our Achievements – Ns2 Projects

