Spin NS2 code
How to implement Spin Protocol Projects using NS2 Simulator code.What is Spin Protocol?Benfits of implementing Spin Protocol Ns2 Code?
SPIN protocols are resource aware and adaptive.SPIN protocols are based on two key mechanisms namely negotiation and resource adaptation.Spin protocol was designed to improve classic flooding protocols and overcome the problems they may cause, for example, implosion and overlap.Major benefit of Implementing spin protocol Ns2 code is of its flexibility.
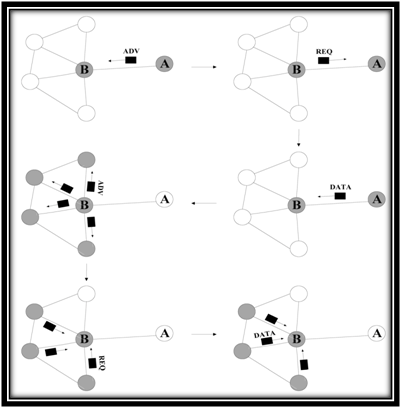
Advantages of spin routing protocol:
- Topological changes are localized since each node needs to know only its single-hop neighbors.
- It gives a factor of 3.5 less than flooding in terms of energy dissipation and meta-data negotiation almost halves the redundant data.
- It supports broadcast transmissions.
- Use meta-data negotiations to eliminate the transmission of redundant data throughout the network.
NS2 Projects Video Output
See our Latest Video Output of Ns2 Projects on Various Domain.
Ns2 Projects
Customized NS2 Projects for B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech/Ms/PhD Scholars.
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots
Ns2 Projects Screen Shots.Regular Update of NS2 Projects Screenshots here!
Sample code for spin routing protocol:
From this code we learn the information of how data packets are handled in spin routing protocols.
PacketHeaderClass::PacketHeaderClass(const char* classname, int hdrlen) :
TclClass(classname), hdrlen_(hdrlen), offset_(0)
{ }
TclObject* PacketHeaderClass::create(int, const char*const*)
{ return (0); }
void PacketHeaderClass::bind()
{
TclClass::bind();
Tcl& tcl = Tcl::instance();
tcl.evalf("%s set hdrlen_ %d", classname_, hdrlen_);
export_offsets();
add_method("offset");
}
void PacketHeaderClass::export_offsets()
{ }
void PacketHeaderClass::field_offset(const char* fieldname, int offset)
{
Tcl& tcl = Tcl::instance();
tcl.evalf("%s set offset_(%s) %d", classname_, fieldname, offset);
}
int PacketHeaderClass::method(int ac, const char*const* av)
{
Tcl& tcl = Tcl::instance();
int argc = ac - 2;
const char*const* argv = av + 2;
if (argc == 3) {
if (strcmp(argv[1], "offset") == 0) {
if (offset_) {
*offset_ = atoi(argv[2]);
return TCL_OK;
}
tcl.resultf("Warning: cannot set offset_ for %s",
classname_);
return TCL_OK;
}}
else if (argc == 2) {
if (strcmp(argv[1], "offset") == 0) {
if (offset_) {
tcl.resultf("%d", *offset_);
return TCL_OK;
}}}
return TclClass::method(argc, argv); }
Journal Support for Research Scholars

Ns2 Projects Work Progress
- MANET – Mobile Ad Hoc Network 95%
- VANET – Vechicle Ad Hoc Netwok 97%
- LTE – Long Term Evolution 78%
- IoT – Internet of Things 90%
- Wireless Sensor Network 89%
- Network Security 89%
- Ns2 Attacks 96%
- Cognitive Radio Network 85%
- Parallel and Distributed Computing 73%
- SDN – Software Defined Networking 95%
- P2P , Video Streaming , Peersim 96%
- IPV4 , IPV6 88%
- 4G Network , 5G Network 80%
- Visual , Underwater Sensor Network 79%
- Multicasting Communication 84%
- Wimax, WiFi 90%
- OFDMA 94%
Our Achievements – Ns2 Projects

